 |
|
 |
|
 |
The etiopathogenesis of idiopathic scoliosis is a still controversial chapter, hence the persistence of the term idiopathic which means that we still do not know the origin of the majority of scoliosis.
|
 |
Some definitions: Etiology corresponds to the factors at the origin of idiopathic scoliosis. Pathogenesis corresponds to the mode of origin of the morbid process. Pathomechanism is the sequence of events in the evolution of its structural and functional changes that result from the pathological process. Etiopathogenesis includes etiology and pathogenesis. Scoliogeny Burwell (2013) proposed this word as a collective name to include: etiology, pathogeny and pathomechanism.
|
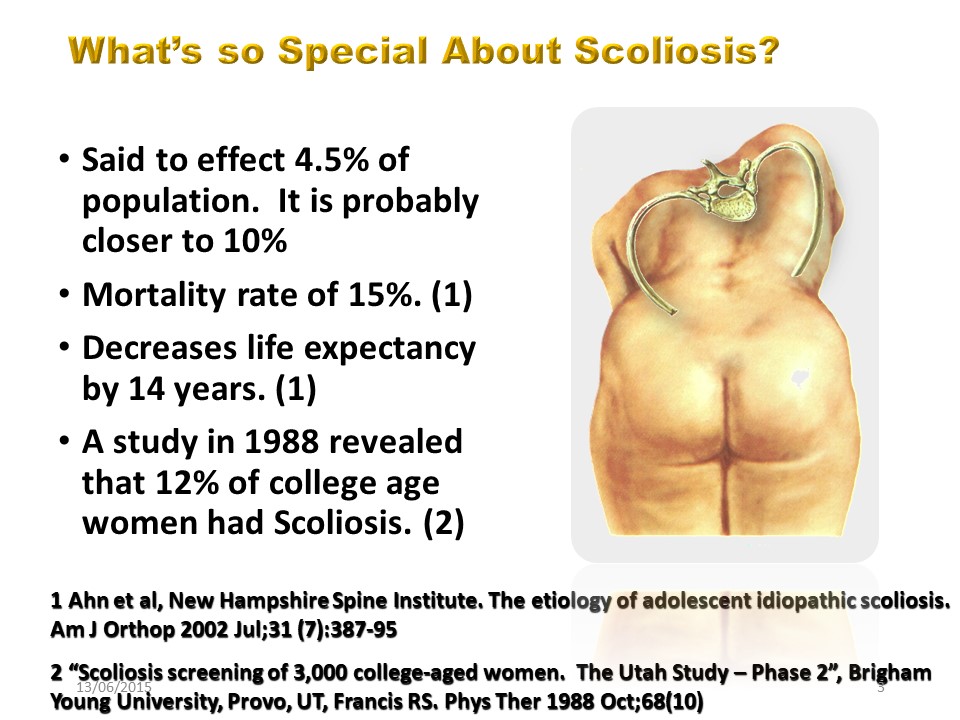 |
Scoliosis is a public health problem that affects at least 4% of adolescents and more than 10% of the population after 60 years. in addition to its frequency scoliosis has consequences on the quality of life and on the lifespan.
|
 |
|
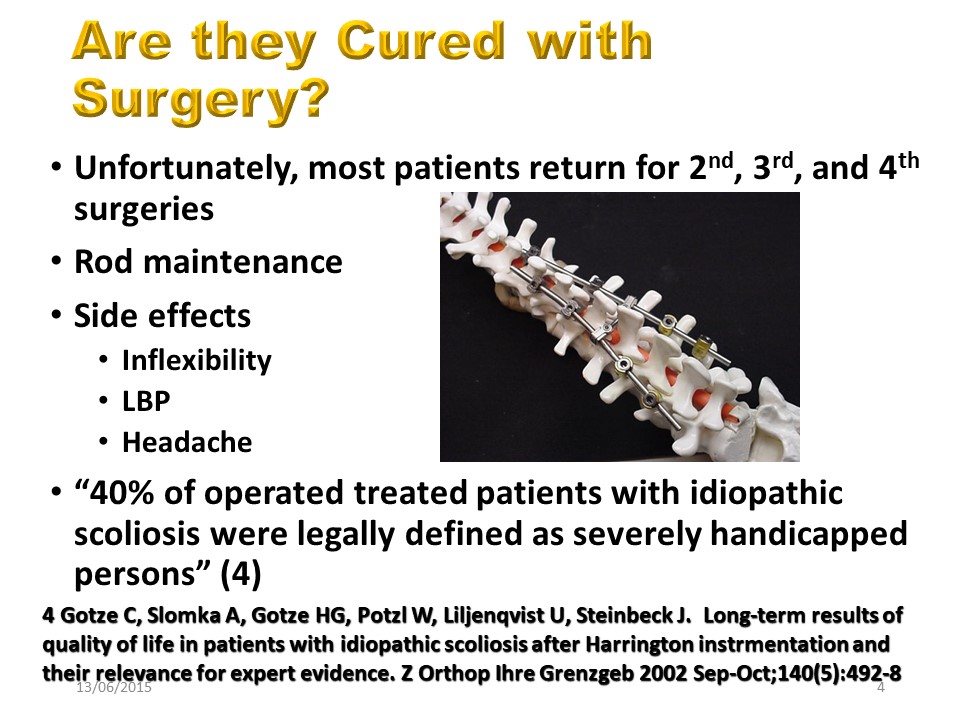 |
Orthopedic treatments are palliative including surgery which often requires multiple interventions over the course of life. The modulus of elasticity of the metal being different from that of the bone. The side effects are important, the spine being made to be mobile and not to be blocked. The latest Swiss publications confirm that 40% of scoliosis operated patients can be defined as disabled.
|
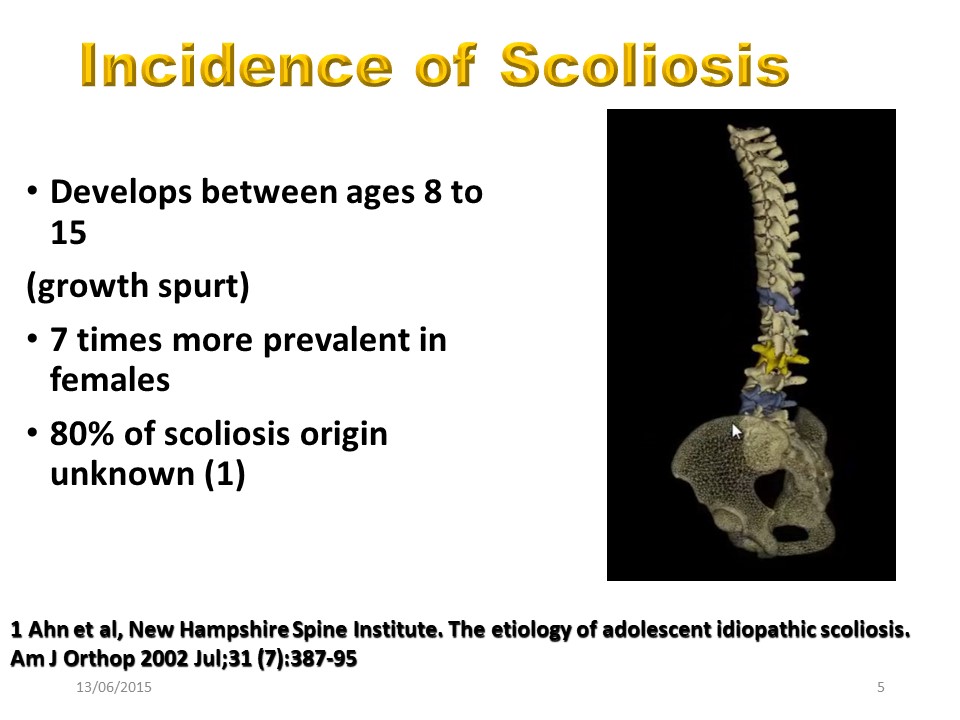 |
Scoliosis essentially evolves during pubertal growth. Beyond 20 °, it is 7 times more frequent in girls and 80% of scoliosis can be defined as idiopathic.
|
 |
Scoliosis essentially evolves during pubertal growth. Beyond 20 °, it is 7 times more frequent in girls and 80% of scoliosis can be defined as idiopathic.
|
 |
If the real cause of idiopathic scoliosis is unknown, there are undoubtedly 2 major elements: genetic anomalies and disturbances in melatonin. Indeed, melatonin is mainly secreted during puberty and the consequences of its deficit approximate to what we note in idiopathic scoliosis.
|
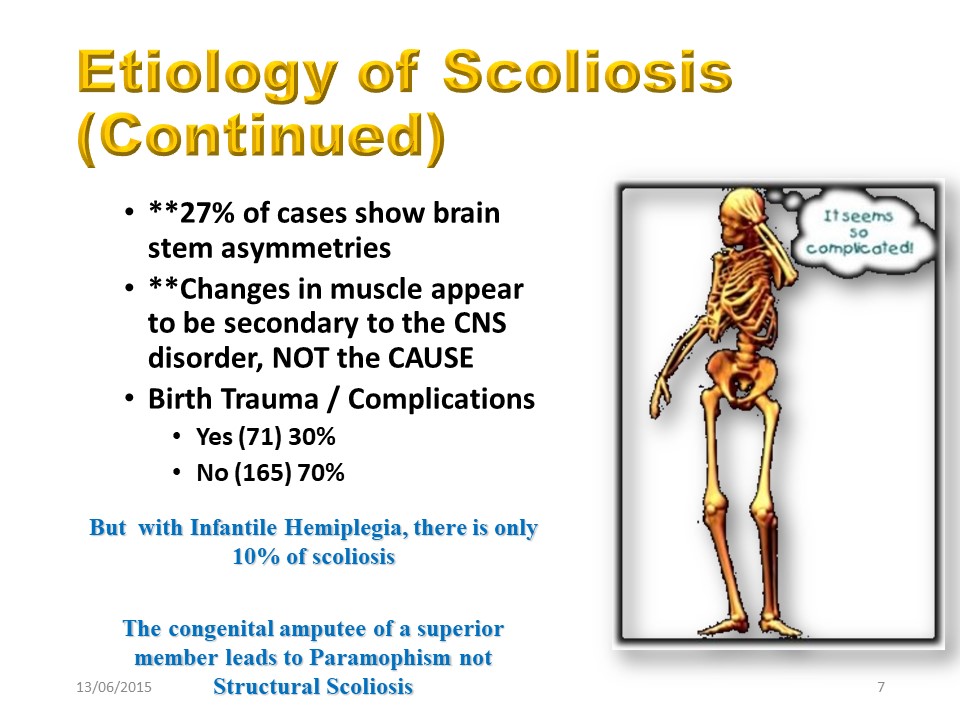 |
There are other anomalies, notably at the neurological level and at the level of the muscles, but which appear more secondary than primitive. It should also be noted that significant asymmetries such as infantile hemiplegia or congenital amputation of an upper limb cause only little structural scoliosis. You have to be "normal" to develop scoliosis.
|
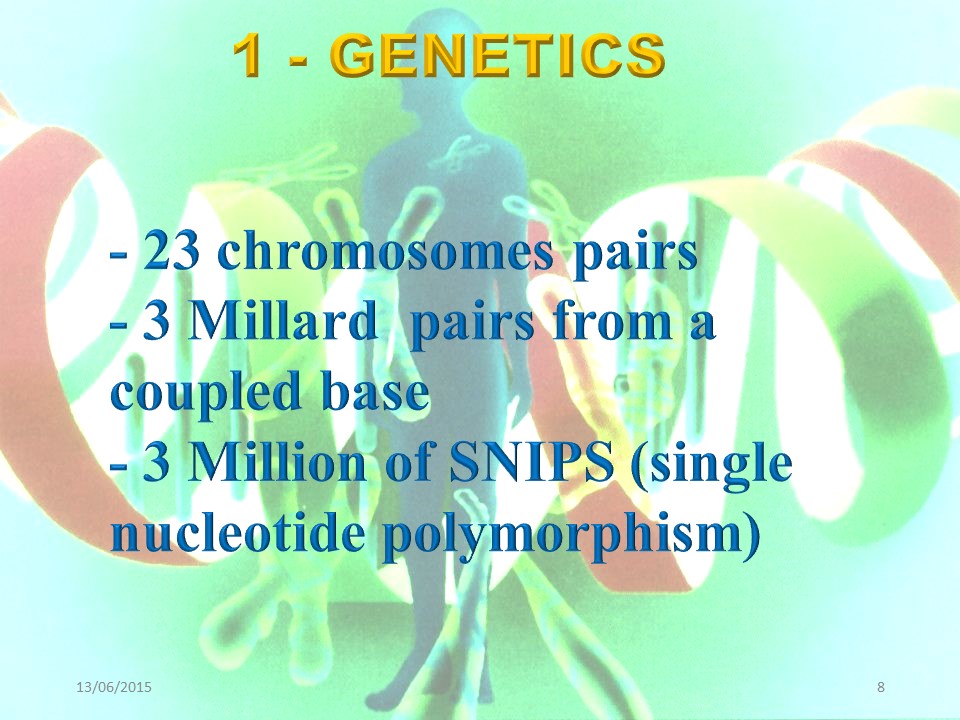 |
In idiopathic scoliosis, an alteration of at least 4 pairs of chromosomes has been found.
|
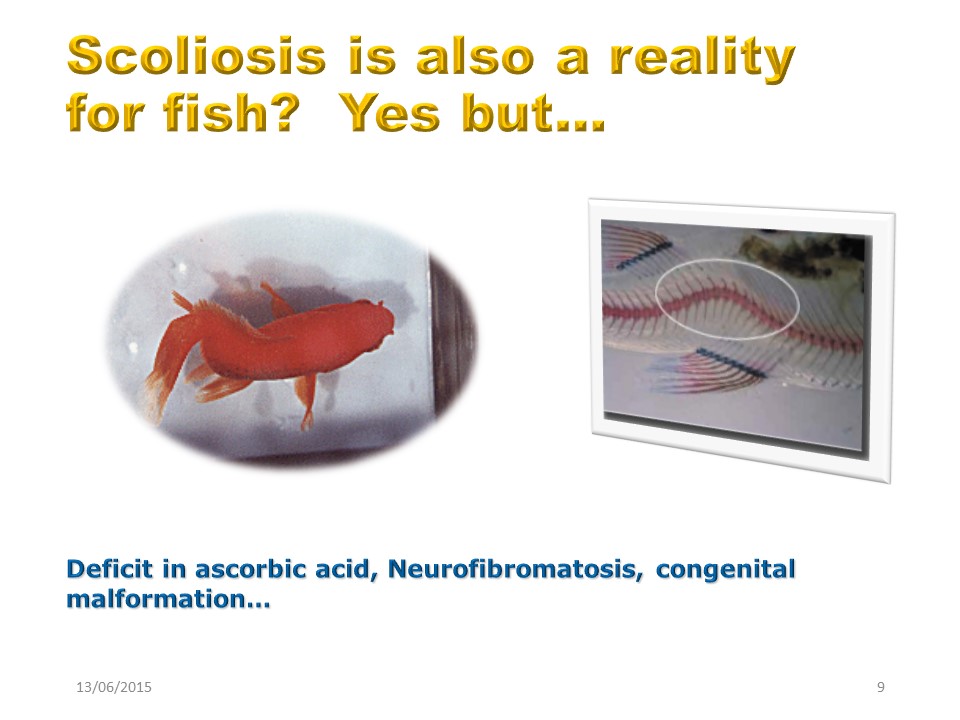 |
The scoliosis is a consequence of bipedia but can also be a reality for fish. But it happens in a deficiency context, deficit is ascorbic acid, neurofibromatosis and congenital malformation.
|
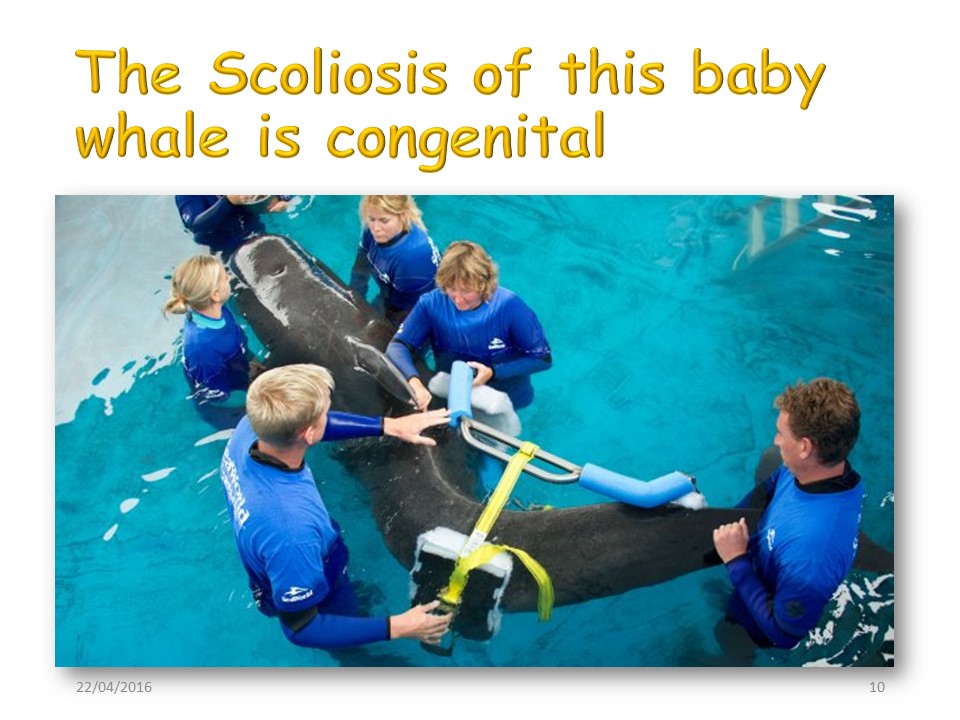 |
In this calf, scoliosis is linked to a congenital vertebral malformation and the 3-point brace made seems very illusory.
|
 |
The flora can also show anomalies . The pine is the straightest tree in the nature except in the russian forest of Kurshskaia Kosà where nazis tested chemical weapons during world war 2.
|
 |
In this case, the genetic disturbance is obvious.
|
 |
We know about a hundred genetic diseases associated with scoliosis. They affect all chromosomes. Idiopathic scoliosis is therefore not linked to an isolated chromosomal abnormality.
|
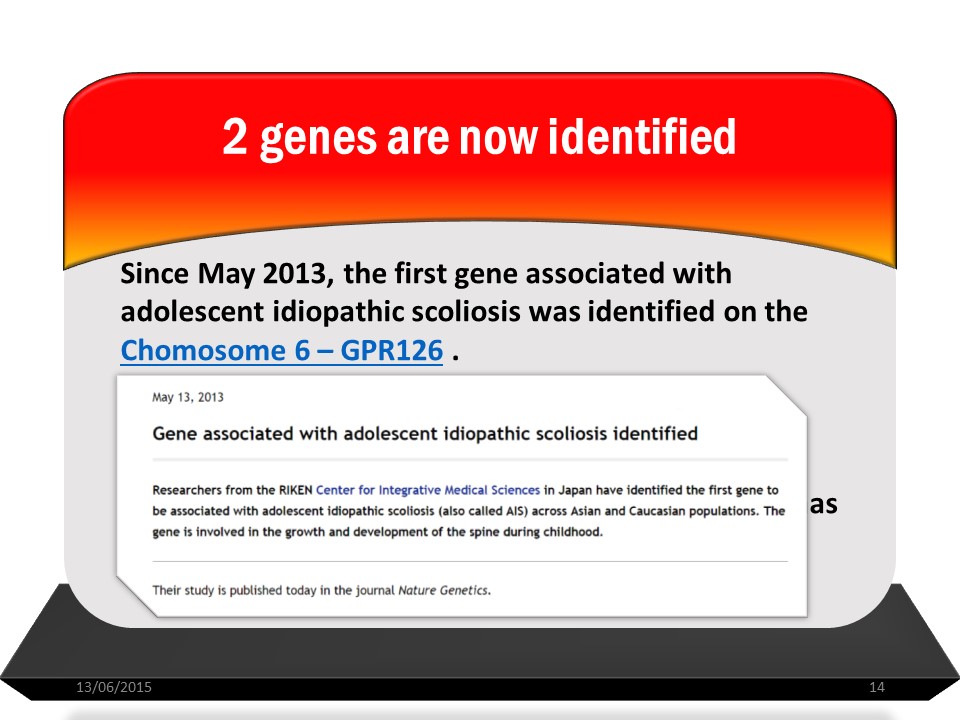 |
The last 2 genes identified are on the one hand GPR126 on chromosome 6.
|
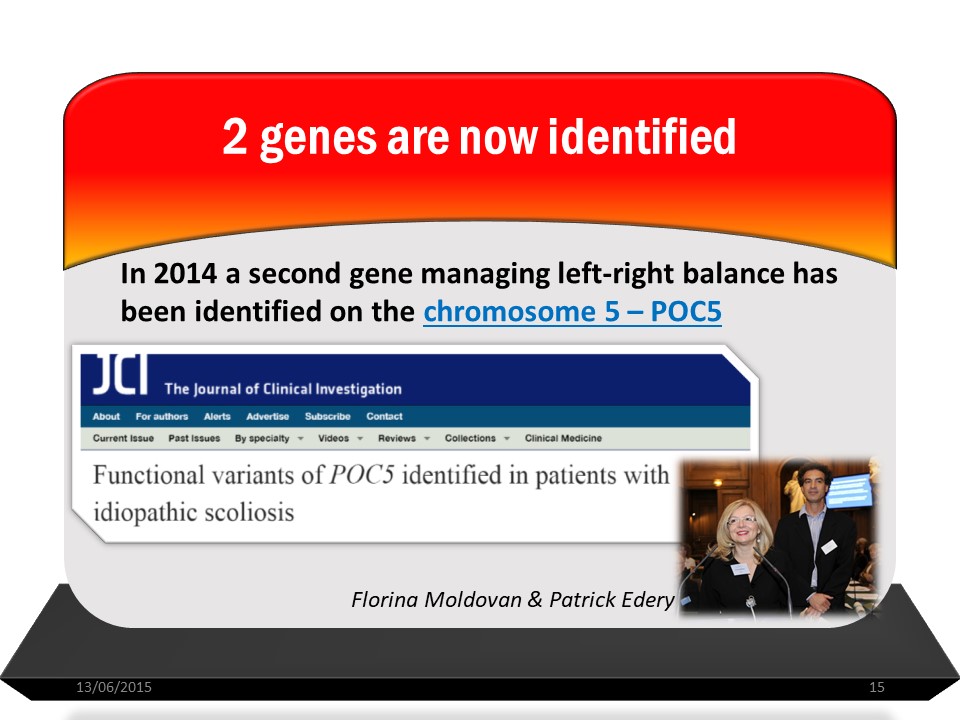 |
and POC5 on chromosome 5. The latter hinders a role in the patient's right / left laterality.
|
 |
The problem is the incidence of the genetic factor. The notion of familiarity is classic in idiopathic scoliosis and verified in clinical practice. Twins, in particular monozygote, allow us to put the genetic factor into perspective
|
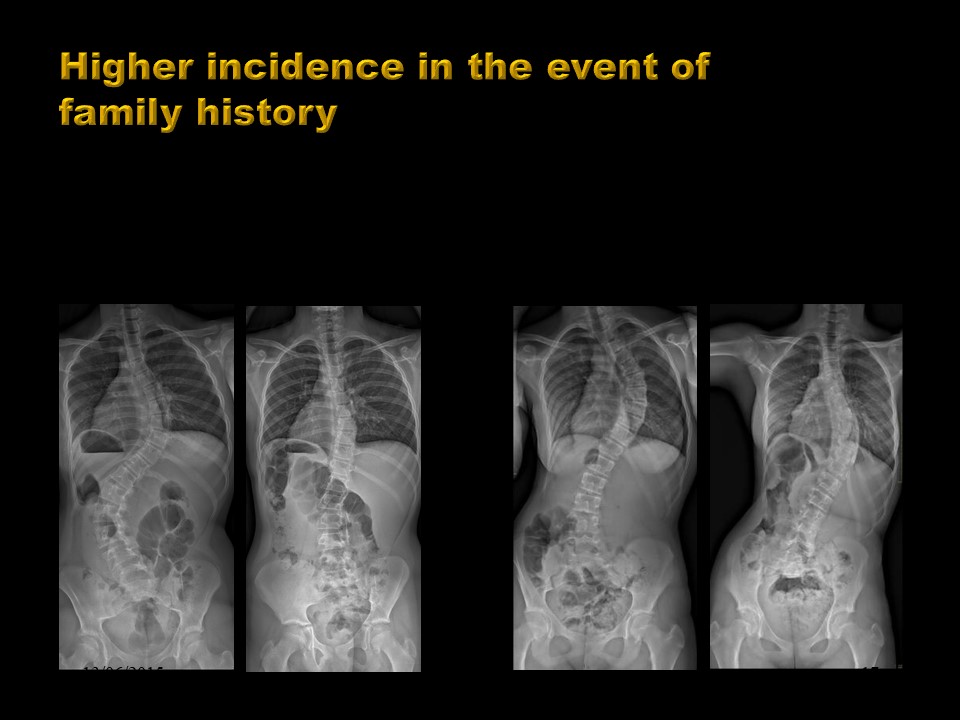 |
.If the existence of scoliosis reaches 90% in monozygotic twins, often the deviation is not identical, although in addition to DNA, the environment is most of the time identical.
|
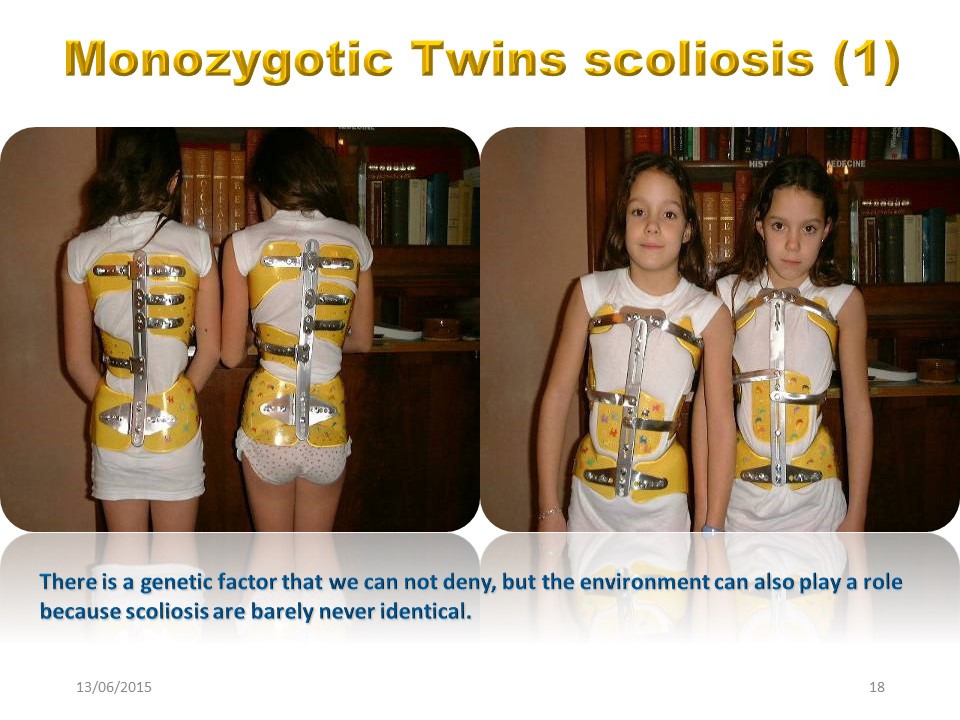 |
These two monozygotic twin children who have the same environment, certainly both have the same brace, but they do not have the same scoliosis.
|
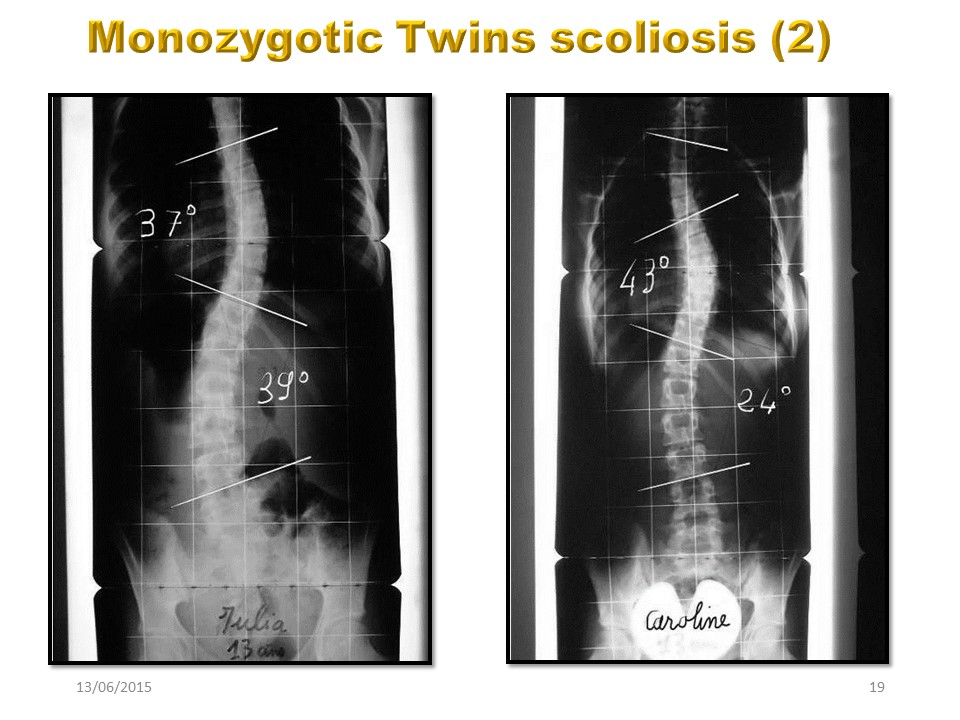 |
Julia has a double major scoliosis, while Caroline has a right thoracic curvature predominant with low lumbar rotation.
|
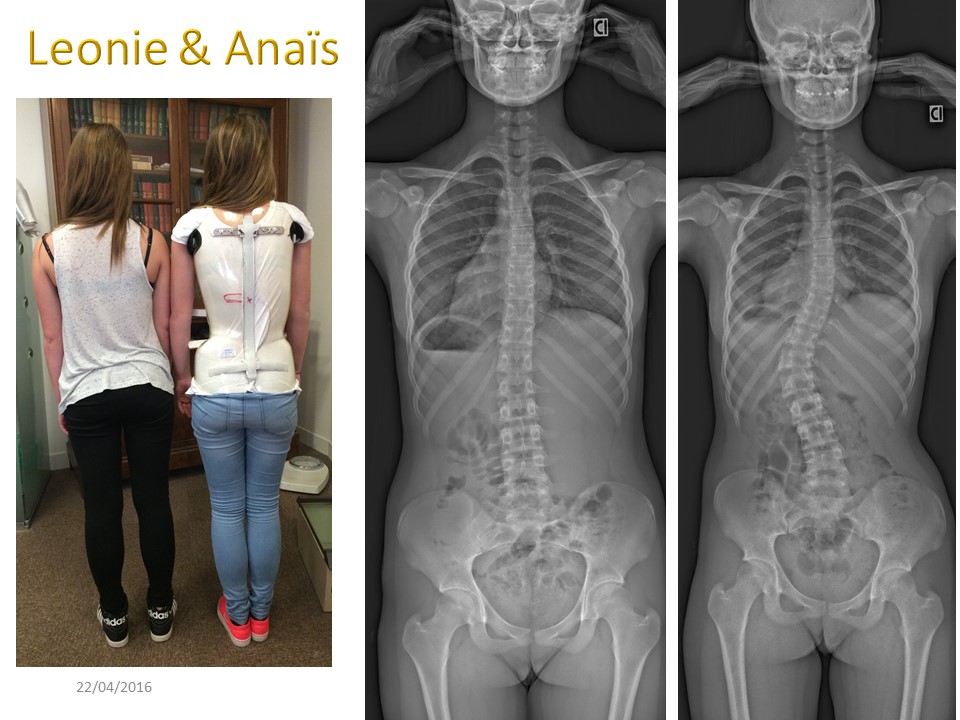 |
Léonie and Anais are also two monozygotic twins. One has thoracolumbar scoliosis justifying the wearing of a brace, the other has no significant deviation. I often use this example to explain that we must be more attentive, but that evolution is not inexorable.
|
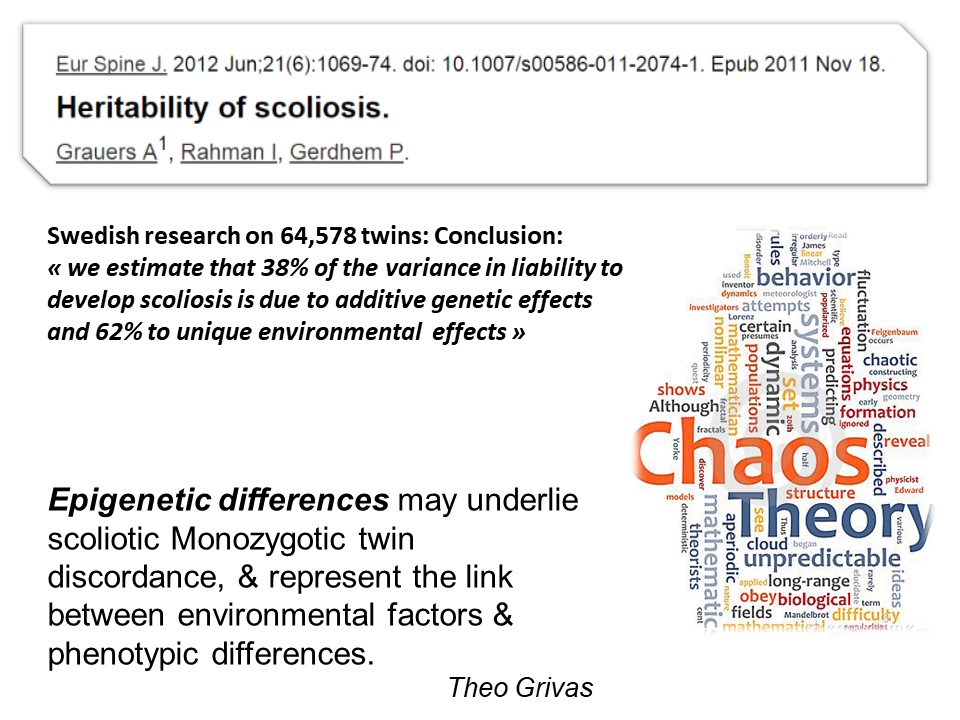 |
A Swedish study considers that genetics explain only 38% of the scoliosis risk, the remaining 62% are linked to the environmental factor. Epigenetic differences may be the cause of this discordance in monozygotic twins, and represent the link between environmental factors and phenotypic differences.
|
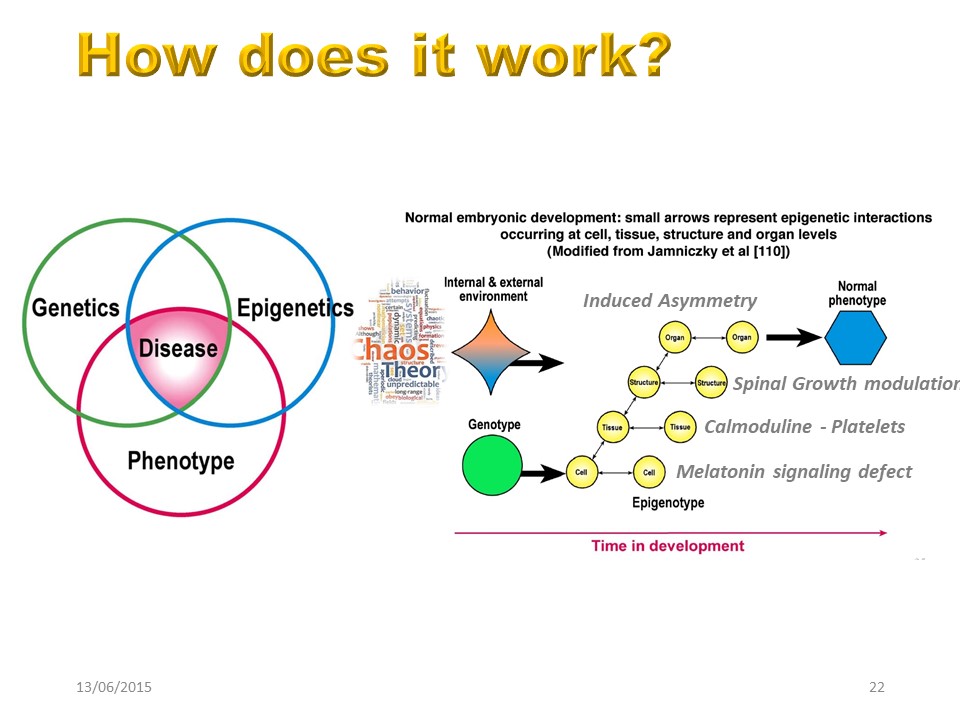 |
There are important interactions between genetics, environment and phenotype to lead to the disease.
|
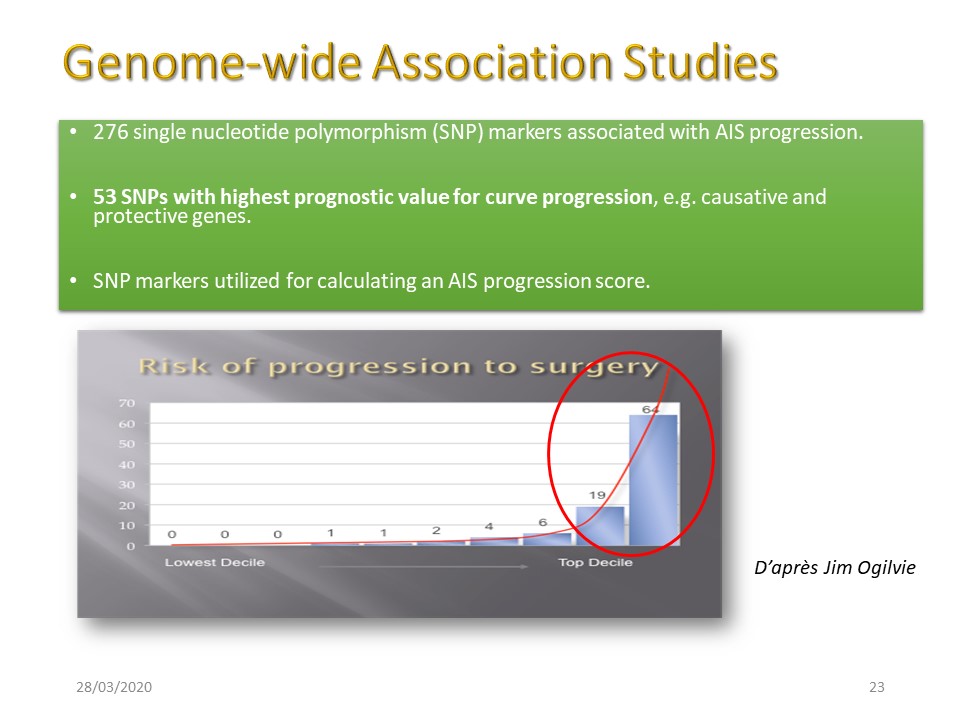 |
Numerous markers are associated with the development of scoliosis and make it possible to calculate a prognosis of progression. However, there is a large gray area where the prognosis is random. In practice, these tests are little used and cannot replace the careful supervision of a child.
|
 |
The intermediate zone in yellow concerns 2/3 of the patients for whom the prognosis is difficult.
|
 |
The study of melatonin is the second pillar of the etiology of scoliosis.
|
 |
This study was initiated by Machida and Dubousset from the observation of bipedal scoliotic chickens after removal of the pineal gland.
|
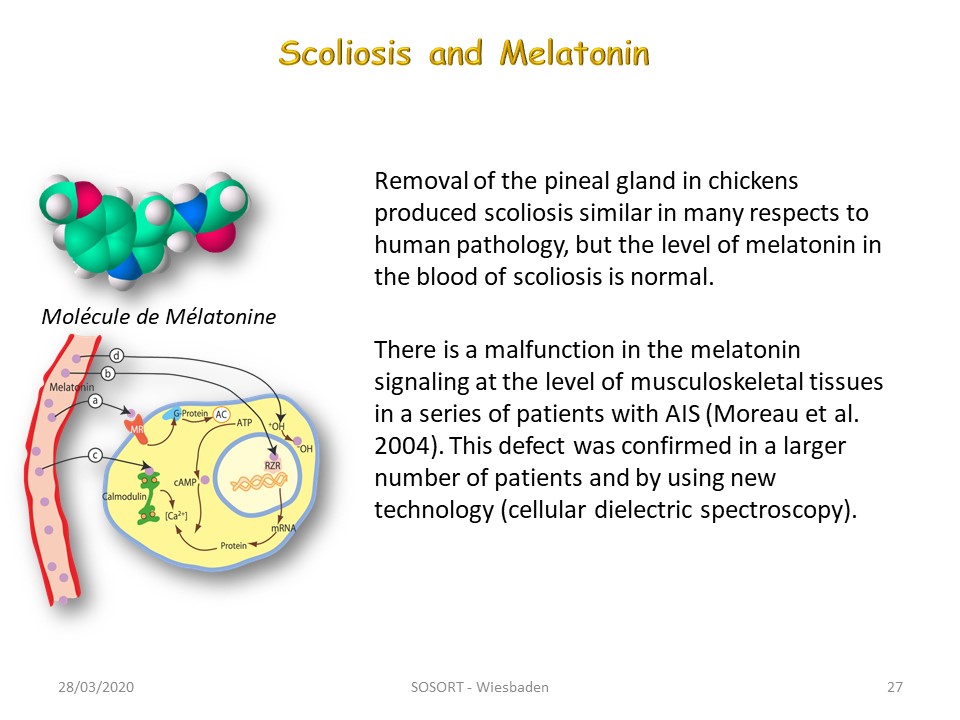 |
In the scoliosis patient, the level of melatonin in the blood is not decreased. In 2004 Moreau highlighted a lack of passage of melatonin at the cellular level linked to a signaling problem.
|
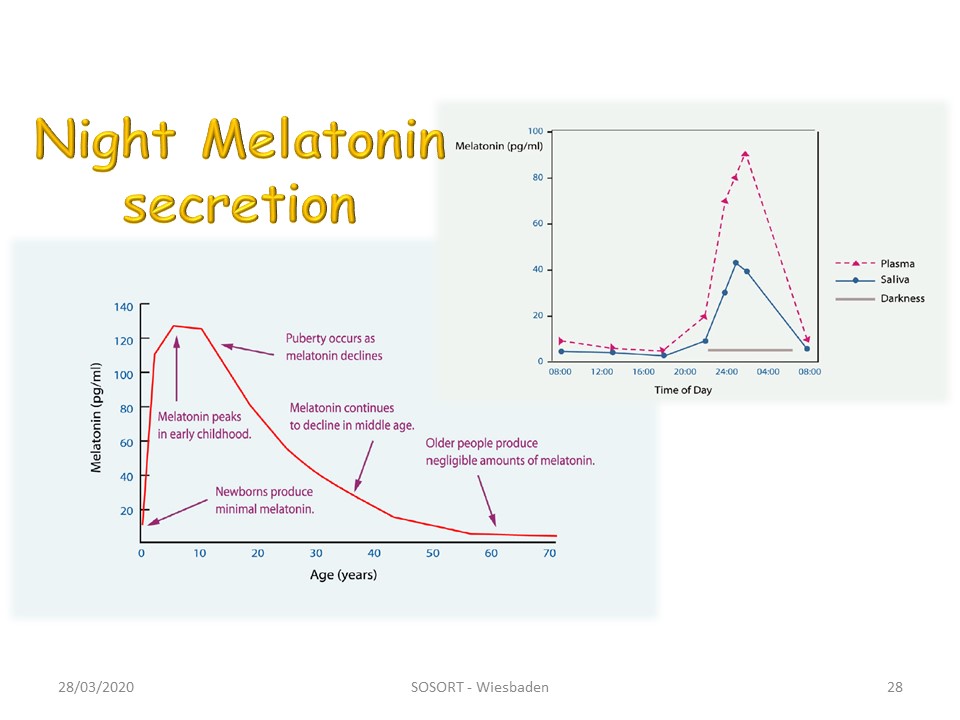 |
Melatonin is the conductor of all growth hormones. The maximum of secretion occurs during pubertal peak. It is secreted during the night which is the main part of the growth.
|
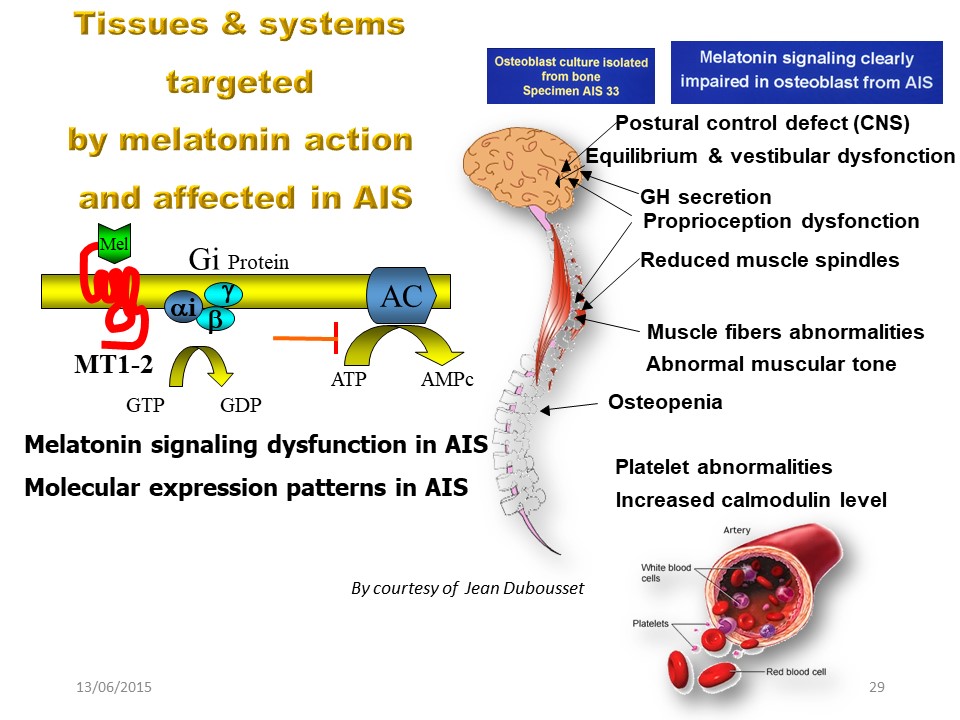 |
A melatonin deficit at the cellular level causes a symptomatology very close to what is observed in scoliosis: Lack of postural control, vestibular and proprioceptive dysfunction, muscle tone anomalies, osteopenia, platelet anomalies with increase in calmodulin level ...
|
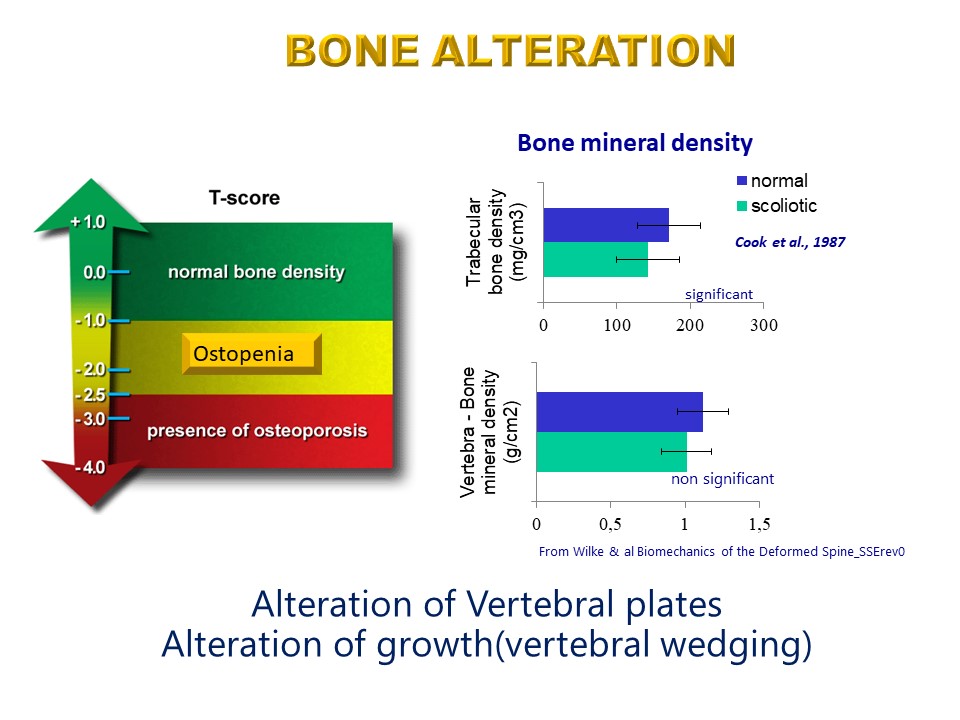 |
Scoliosis is associated with bone changes with loss of the number of trabeculae in women and thinning of the number of trabeculae in men. This results in a defect in the resistance of the cortex of the vertebral bodies which will promote vertebral wedging at the apex of scoliosis.
|
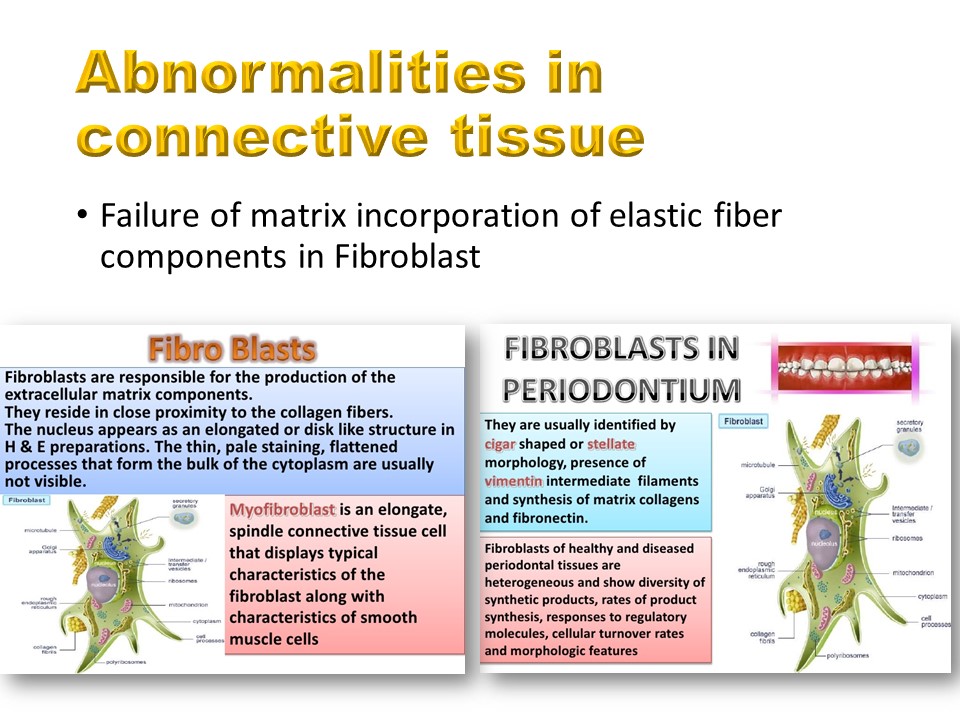 |
The anomalies of the connective tissue and in particular of the fibroblast corresponding to a defect of incorporation of the elastic elements in the matrix. There is therefore a bone-soft tissue coupling explaining the advantage of plastic deformation in conservative orthopedic treatments.
|
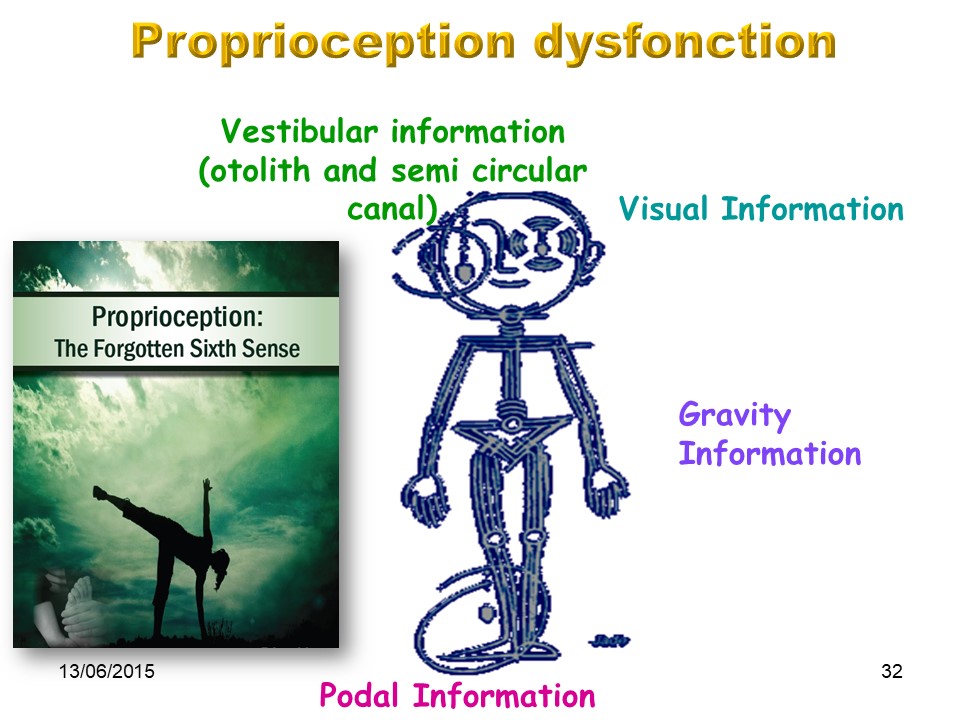 |
Almost all the elements of the extra-pyramidal system will be disturbed, from the peripheral sensors to the vestibular integration centers.
|
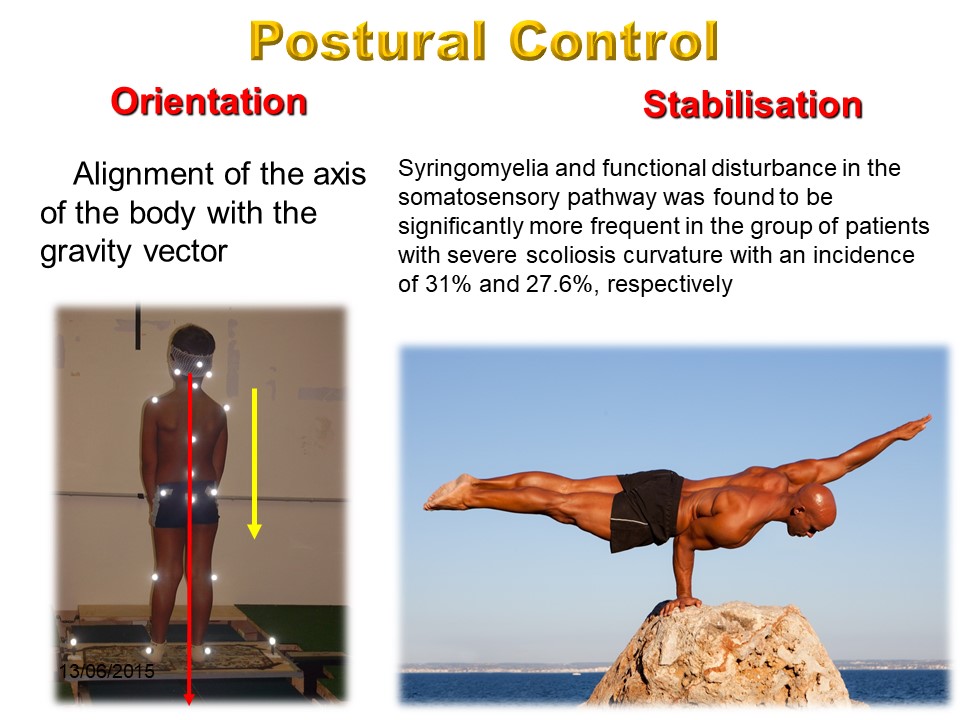 |
Two functions of postural control, the orientation and stabilization functions can be distinguished. Under static condition, to control the posture of the whole body consist in choosing a vertical orientation and to maintain this vertical orientation despite the perturbing effects of gravity. These two functions are disturbed in scoliosis with misalignment of the line of gravity and defects of deep sensitivity with approximately 30% of syringomyelia.
|
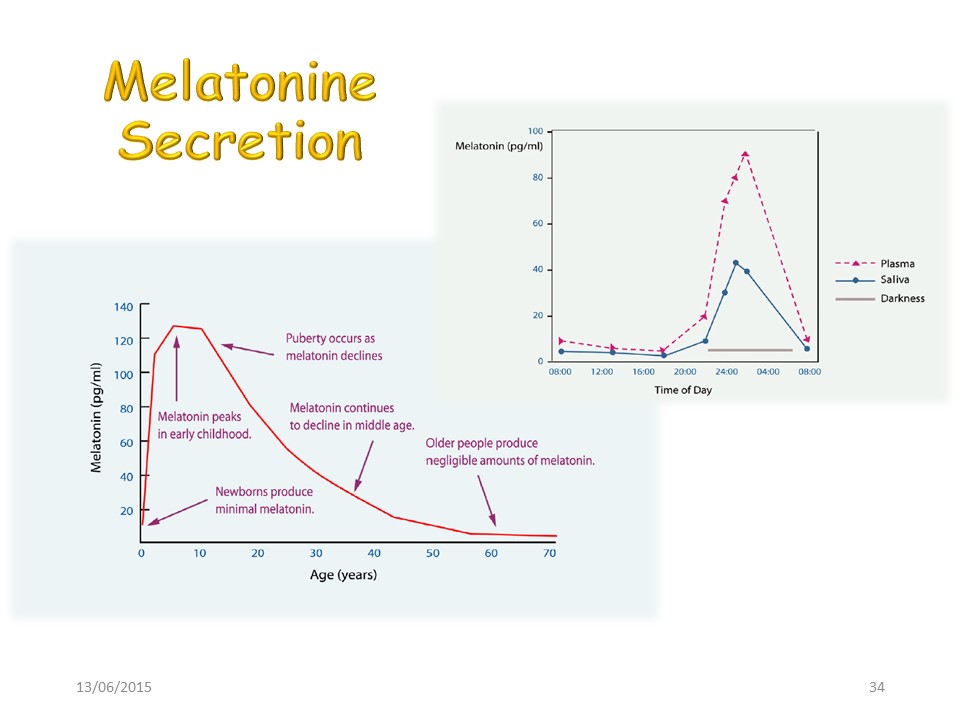 |
We have already seen that melatonin is secreted overnight and at most during puberty.
|
 |
Unfortunately, research on the failure to melatonin signalising, despite the use of cellular dielectric spectroscopy to measure ostéopontine, did not allow 16 years later to reach a prognosis of scoliosis progression.
|
 |
The first results were, however, very promising.
|
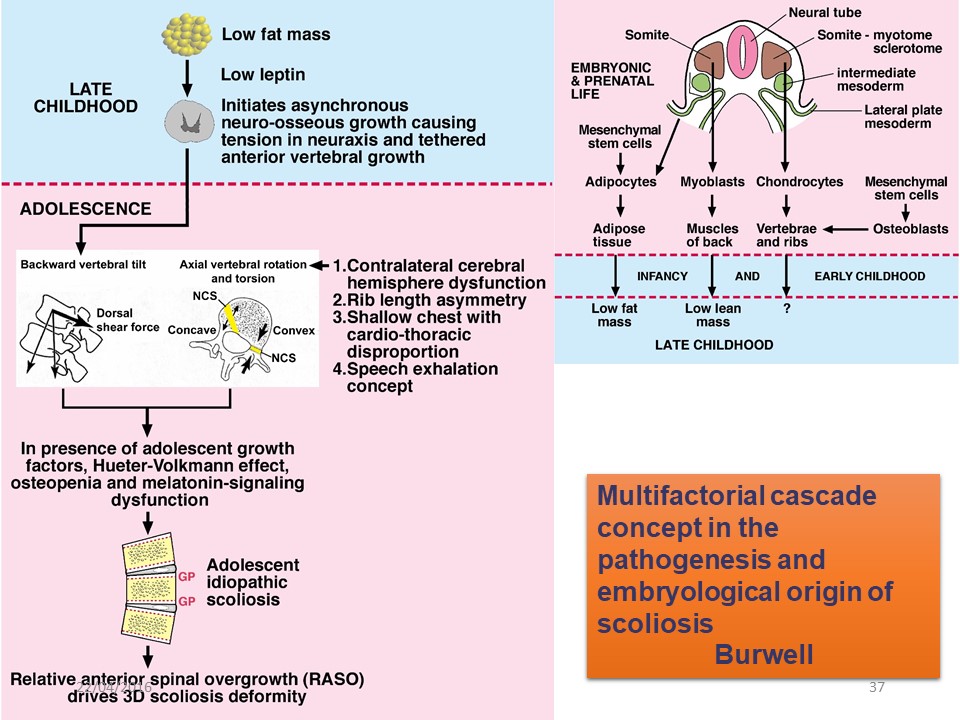 |
This Burwell diagram sums up the whole paradox of idiopathic scoliosis that we know better and better, but whose evolutionary prognosis below 20 ° remains impossible to predict.
|
 |
This Burwell diagram sums up the whole paradox of idiopathic scoliosis that we know better and better, but whose evolutionary prognosis below 20 ° remains impossible to predict.
|
 |

To register for Certification, please contact SSOL

|